Business Measurement Sophistication with Howard Diesel
Executive Summary
This webinar outlines the importance of utilising measurement frameworks in business decision-making, understanding the Balanced Scorecard and OKR frameworks, and identifying North Star metrics. Howard Diesel discusses the impact of metrics on business and agile teams, the alignment of business strategy and data metrics, and the importance of countermeasures in agile team performance. The webinar discusses key business metrics and analysis concepts, big data context diagrams and analytics, and the uncertainty framework and team structure. Howard stresses that by understanding and utilising these concepts effectively, businesses can measure performance and culture, align data with business metrics, and ultimately achieve their strategic goals.
Webinar Details
Title: Business Measurement Sophistication
Date: 22 January 2021
Presenter: Howard Diesel
Meetup Group: Data Executives
Write-up Author: Howard Diesel
Contents
Business Decision-Making Sophistication.
Decision-Making Frameworks and Performance Metrics.
Understanding the Balance Scorecard and OKR Frameworks.
Business Culture and Strategy.
OKR and Customer Intimacy in Business Strategy.
Key Concepts of OKRs and North Star Metrics.
Importance of Identifying North Star Metrics.
North Star Metrics and Pirate Funnel
Using Frameworks for Data Management
Utilising Metrics and Measurement Systems.
Measuring Performance and Culture.
The Impact of Metrics on Business and Agile Teams.
Importance of Counter Measures in Agile Team Performance.
Metrics and Strategies for Startup Companies.
Key Concepts in Business Metrics and Analysis.
Big Data Context Diagram and Analytics.
Alignment of Business Strategy and Data Metrics.
Aligning Data with Business Metrics.
Importance of Metrics and Financial Value in Data Management
Aligning Metrics and Value Propositions in Business Strategy.
Importance of Value Proposition and Correct Metrics in Business.
The Uncertainty Framework and Team Structure.
Building Team Culture and Decision-Making in Business.
Business Decision-Making Sophistication
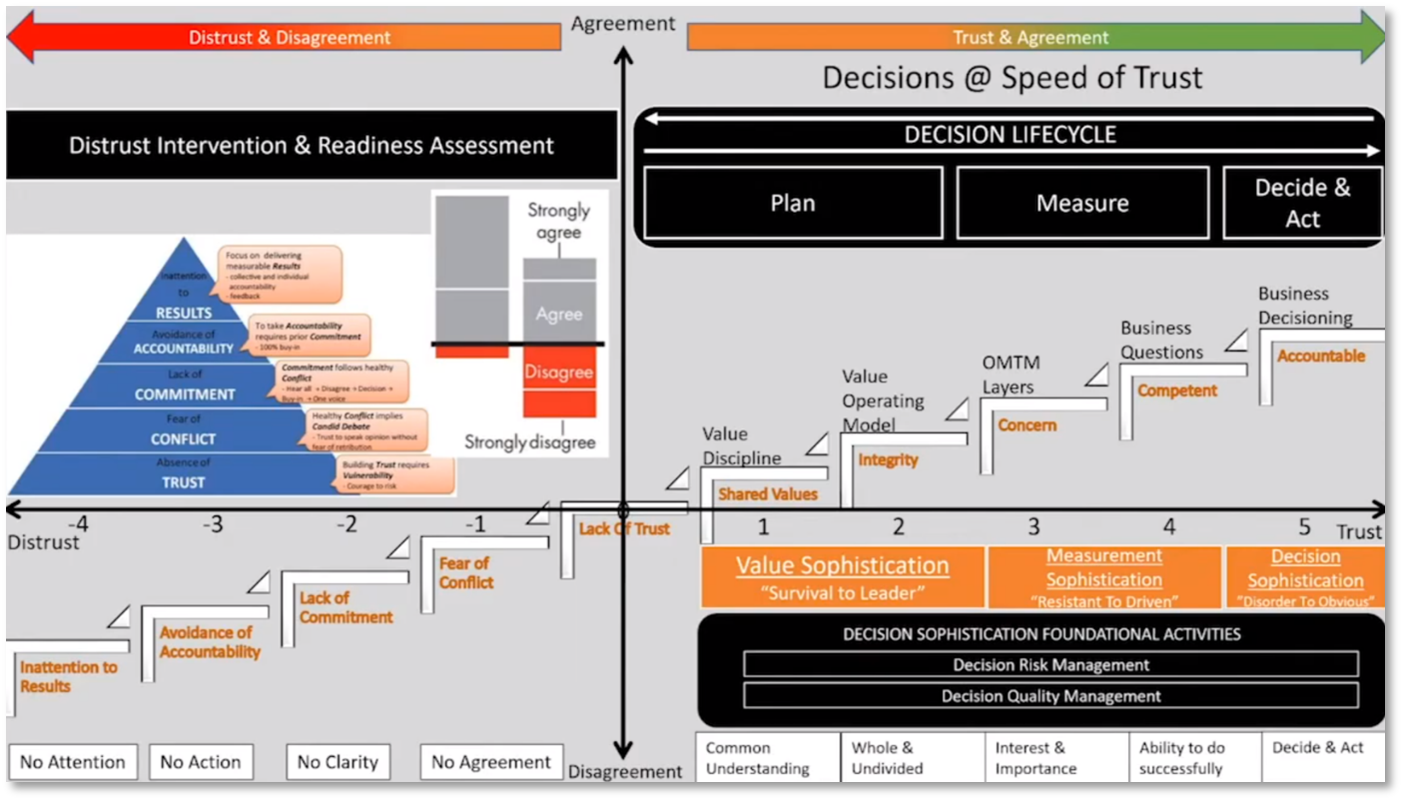
Howard Diesel emphasises the importance of having the right metrics to make informed decisions. There are three areas of sophistication - value, measurement, and decision. Howard notes that high-performing companies utilise business decision-making sophistication to their advantage. The challenge of data distrust and the need to build trust to move along the decision cycle is discussed.
Figure 1 The webinar's discussion, make sure to join us to not miss out on future discussions
Figure 2 Measurement Frameworks
Figure 3 Decision diagram
Decision-Making Frameworks and Performance Metrics
Disagreements can hinder decision-making, but countries with strong control and minimal disagreement can make decisions faster. The impact of diversity and disagreement on decision-making is a topic of discussion. Still, it is important to consider the reasons for disagreement, such as a lack of trust in data or personal beliefs. Disagreement can also prolong decision-making processes within an organisation. Several frameworks, such as Jobs to be Done, OKRs, Balanced Scorecard, and North Star, are available for decision-making. Still, it is essential to prioritise having the right metrics over the specific framework used.
Understanding the Balance Scorecard and OKR Frameworks
The Balanced Scorecard is a management and strategy framework comprising four key areas: learning and growth, customers, financial data, and internal business processes. The strategy sits across all four areas and can be implemented with each area working independently or with a roll-up structure. Stakeholder perspectives may be used instead of customer perspectives. Analysis of financial data involves the investigation of knowledge resources, training, and operational management. Customer perspectives gauge customer satisfaction with price and depend on the value discipline. Value sophistication involves choosing a discipline, operating model, and determining the north star. The combination of metrics and value disciplines can be considered based on the intended audience and goals.
Figure 4 Measurement Frameworks
Figure 5 What is a Balanced Scorecard (BSC)?
Business Culture and Strategy
Considering culture in business strategy is paramount, particularly regarding customer intimacy, product leadership, and operational excellence. Customer intimacy involves building products around customer needs, while product leadership focuses on creating the best product for the best price. Operational excellence prioritises inventory turns, scale, and throughput. Each of these strategies requires a different approach to business and customer satisfaction, with culture and strategy influencing each other.
Figure 6 What is a Balanced Scorecard (BSC)? Including customers and financial data
OKR and Customer Intimacy in Business Strategy
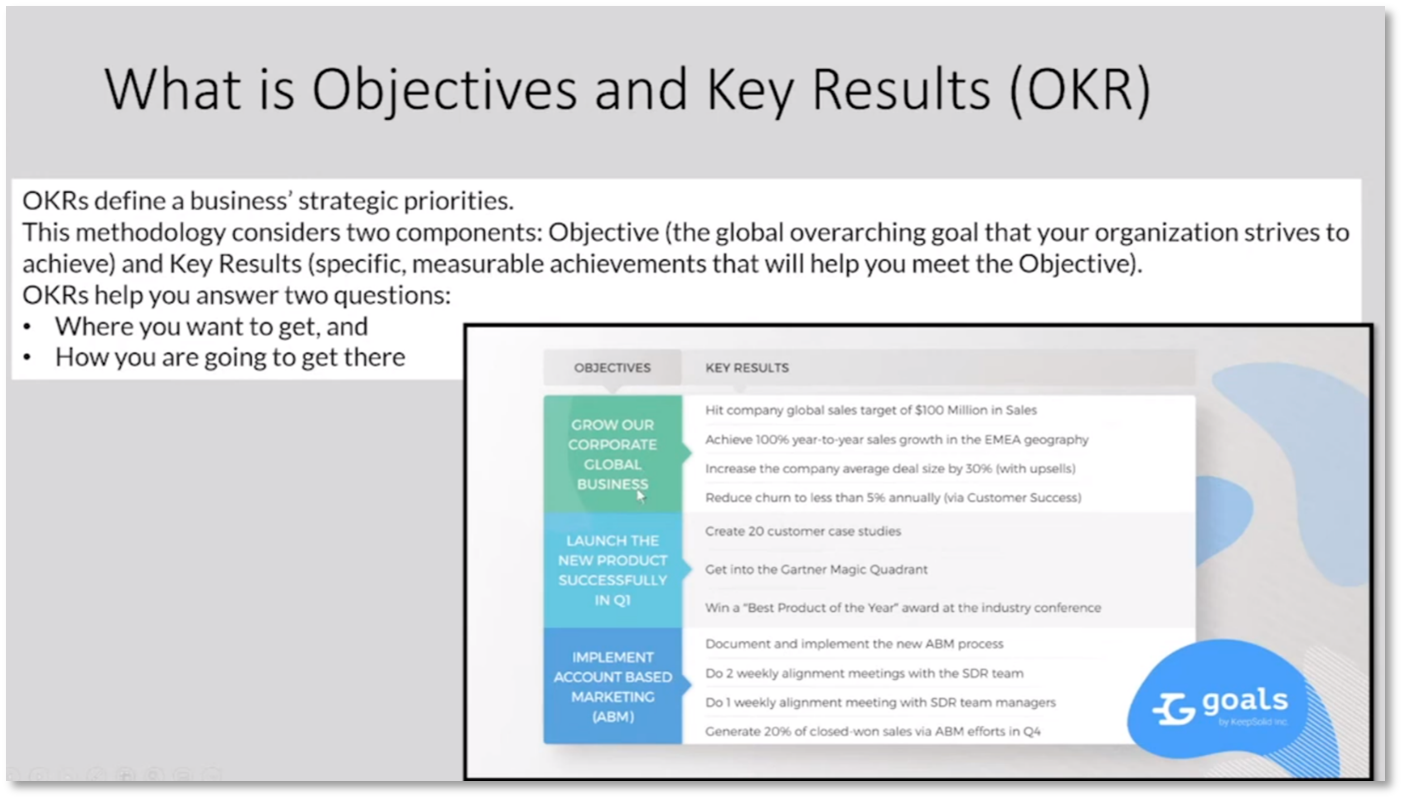
Customer intimacy is an approach that involves creating an ecosystem to enhance technology and meet customer needs by listening to them. Objective and Key Results (OKR), is a strategy for defining global business goals and measurable achievements, which involves defining overall objectives and specific measurable achievements to reach them. OKR is more agile than the balanced scorecard approach and focuses on short-term achievements, making it ideal for setting targets for the next period. It includes global business objectives and key results related to sales growth and reducing churn.
Figure 7 What is Objectives and Key Results (OKR)
Key Concepts of OKRs and North Star Metrics
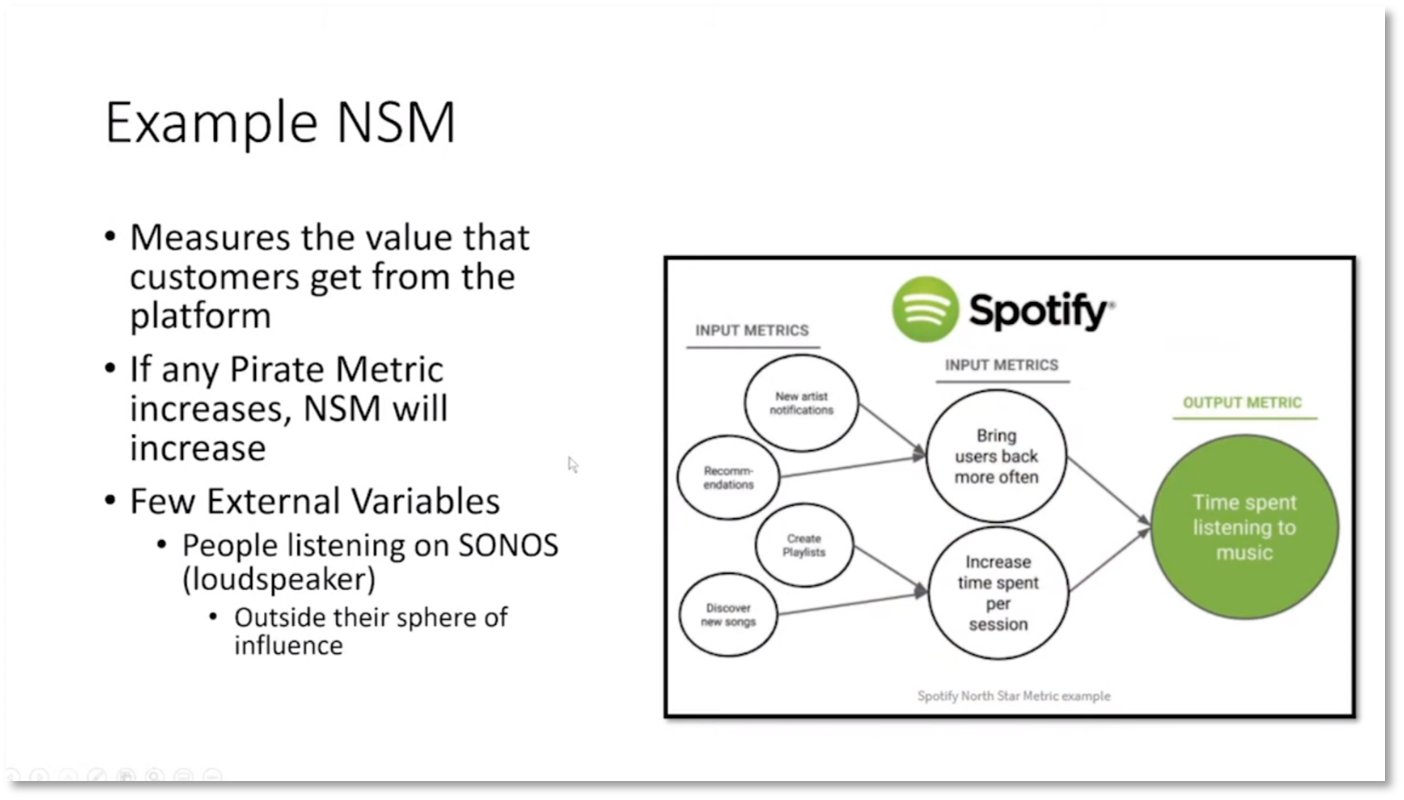
OKRs are objectives with a specific time frame and focus on what needs to be achieved within that period. The North Star metric is a crucial metric that reflects a company's core value and should be the primary focus for success. For example, Spotify's North Star metric is 'listening hours,' which is relatable and understood by everyone in the organisation. This metric works with the 'One Metric That Matters' and the 'Pirate Funnel' to align efforts and priorities across the organisation. Focusing on a single key area allows teams to see progress, create a feedback loop, and accelerate initiatives, leading to greater accountability. Developing a North Star metric involves an eight-step process that focuses on when the customer is satisfied, aligning with the 'jobs to be done' concept.
Figure 8 What is North Star Metric (NSM)
Importance of Identifying North Star Metrics
A key aspect of measuring success in a product or service is the North Star Metric, which indicates when customers achieve the intended result. This metric must align with the overall value provided to customers and be measurable monthly to avoid data challenges and accurately assess performance. For instance, a training company's North Star Metric should consider not just completing the training but also receiving recognition, such as certification or financial and role recognition. Failing to measure the North Star Metric can lead to significant losses, as demonstrated by a trucking company that suffered losses due to the inability to measure progress and performance until six months into the contract.
Figure 9 Choosing a North Star - 8 Steps
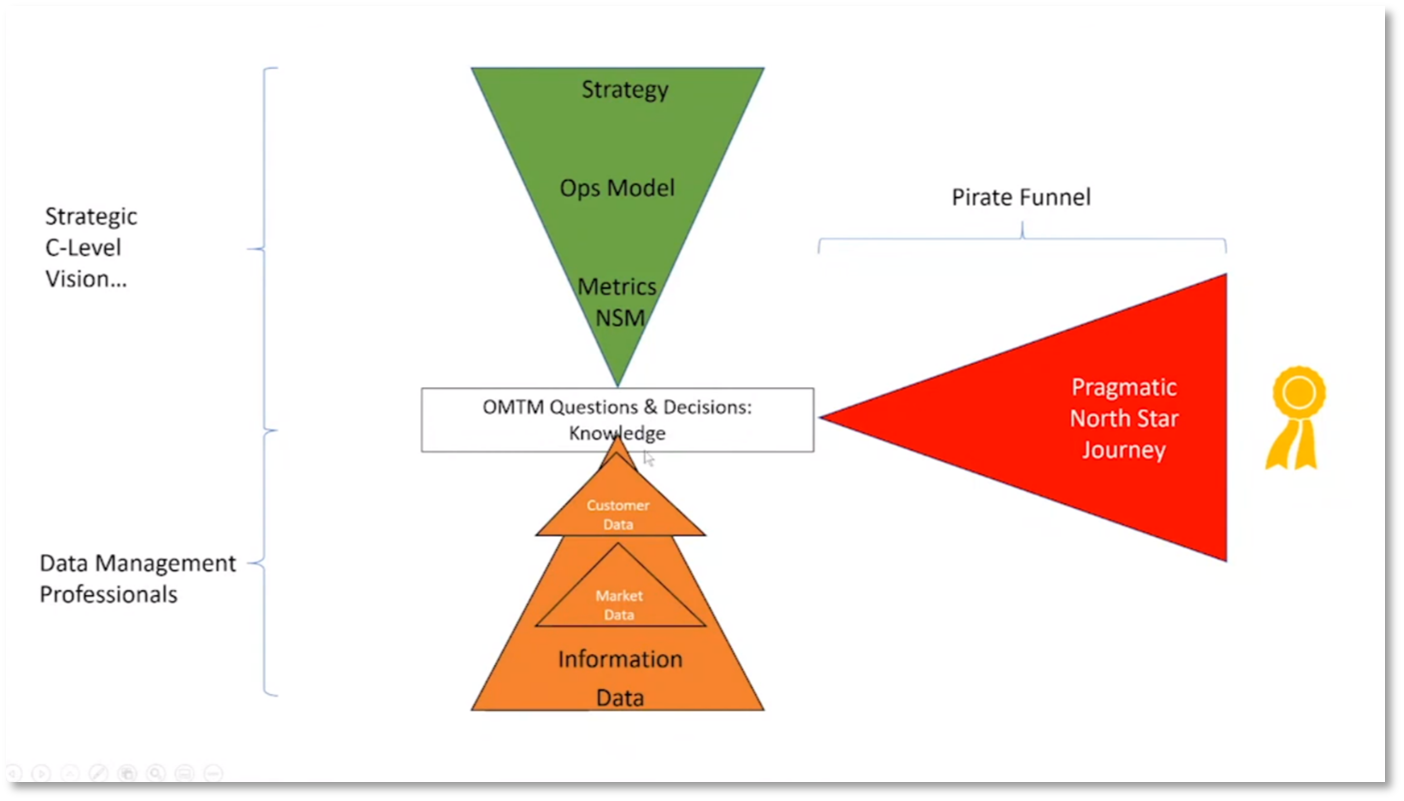
North Star Metrics and Pirate Funnel
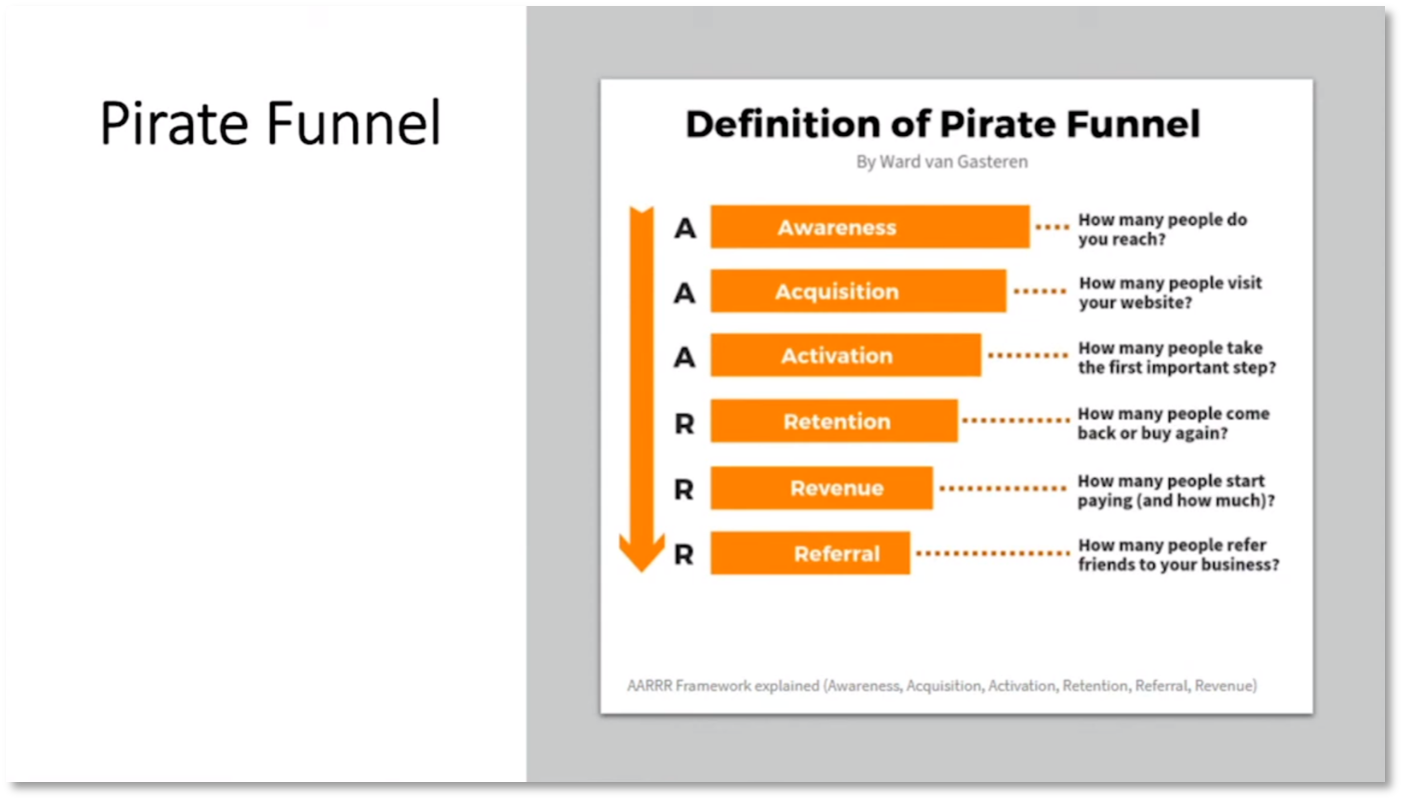
The company fell short of their target budget by 12 million rand, causing embarrassment. It is important to prioritise frequency and minimise external factors. A north star metric should be measurable with data to validate it. Howard notes that Spotify uses time spent listening to music as their north star metric with input metrics of increasing user retention and time spent per session. External variables should be considered, such as people listening to speakers outside the company's control. The Pirate funnel measures product performance and customer lifecycle, including customer awareness, acquisition, retention, and lifetime value. The funnel helps identify bottlenecks in the customer journey through data measurement across different areas.
Figure 10 Example of North Star Metrics
Figure 11 Definition of Pirate Funnel
Using Frameworks for Data Management
Howard explores a case where a company faced challenges retaining customers despite an efficient activation process. The bottleneck was moving from revenue to retention due to low customer lifetime value and high churn rate—multiple frameworks addressed this issue, including a data management operating model and the balanced scorecard. The latter helped identify important metrics and deliver value to stakeholders, making close to 200-300 metrics specified across financial, internal processes, and training levels.
Figure 12 Bottleneck Research
Figure 13 Differences: Designed for Different Purposes
Utilising Metrics and Measurement Systems
The balance scorecard and OKRs are effective tools for understanding and measuring important aspects of an organisation, including financial, internal processes, and training levels. While OKRs are quick and transparent, connecting them with relevant departments and organisational memory is crucial to making meaningful connections. Additionally, setting metrics can motivate but should be carefully managed to avoid creating a negative culture.
Measuring Performance and Culture
When using metrics to reward employees, it's important to consider the wider operating model and culture and be agile and willing to tweak metrics as necessary. Culture is defined by what's measured, so it's crucial to ensure that metrics are aligned with company values and goals. Rewards can significantly impact end results across various disciplines, so measuring effectively is essential for future process improvements. Careful consideration is required to avoid negative impacts resulting from quick decisions on metrics, and sometimes, it's necessary to put metrics on pause and reassess the measurement approach.
The Impact of Metrics on Business and Agile Teams
A case study on Gillette's sales revealed that customers were waiting until the end of the quarter to receive discounts, leading to fluctuations in sales. Consequently, Gillette decided to stop offering discounts at the end of the quarter. It is essential to ensure that specific metrics do not significantly impact a business's bottom line. Instead of removing or hiding metrics, rewarding appropriately across a wide range of metrics is crucial. Some agile teams measure a lot but do not show the measurements to the team to avoid undue pressure or gaming of the system. There is a fine balance between making targets visible and creating negative responses or focusing on the wrong things, such as increasing lines of code that do not necessarily improve the product. Having the appropriate funnel to show progress and make everyone aware of the team's challenges is important.
Importance of Counter Measures in Agile Team Performance
The agile team's unique version of agile was evaluated, and measures were implemented to monitor their performance with various metrics. Countermeasures were deemed crucial in maintaining quality and performance, especially with regard to customer data and sales metrics, as they can prevent negative impacts. The team utilised the balanced scorecard to track and manage metrics and ensure a comprehensive view of performance. Additionally, OKR provides flexibility and sets a clear destination, allowing for cohesive measurement of performance metrics.
Figure 14 From NOWHERE to your NORTH STAR
Metrics and Strategies for Startup Companies
In startup companies, the primary focus is to get people registered on the platform, with a key metric being churn rates to understand what is important at a given time. The North Star, a high-level, long-term, and aspirational goal, helps identify and address specific issues while balancing other measurements. Utilising the balanced scorecard and OKRs adds flexibility and immediate time frames to align the North Star with the value proposition. Jobs to be done are linked with OKRs, and a hierarchy to map across departments and projects, along with the pirate funnel for the product, helps coordinate and manage startup company operations.
Figure 15 Vision, Mission and Values
Figure 16 Role of Big Data and Data Science
Key Concepts in Business Metrics and Analysis
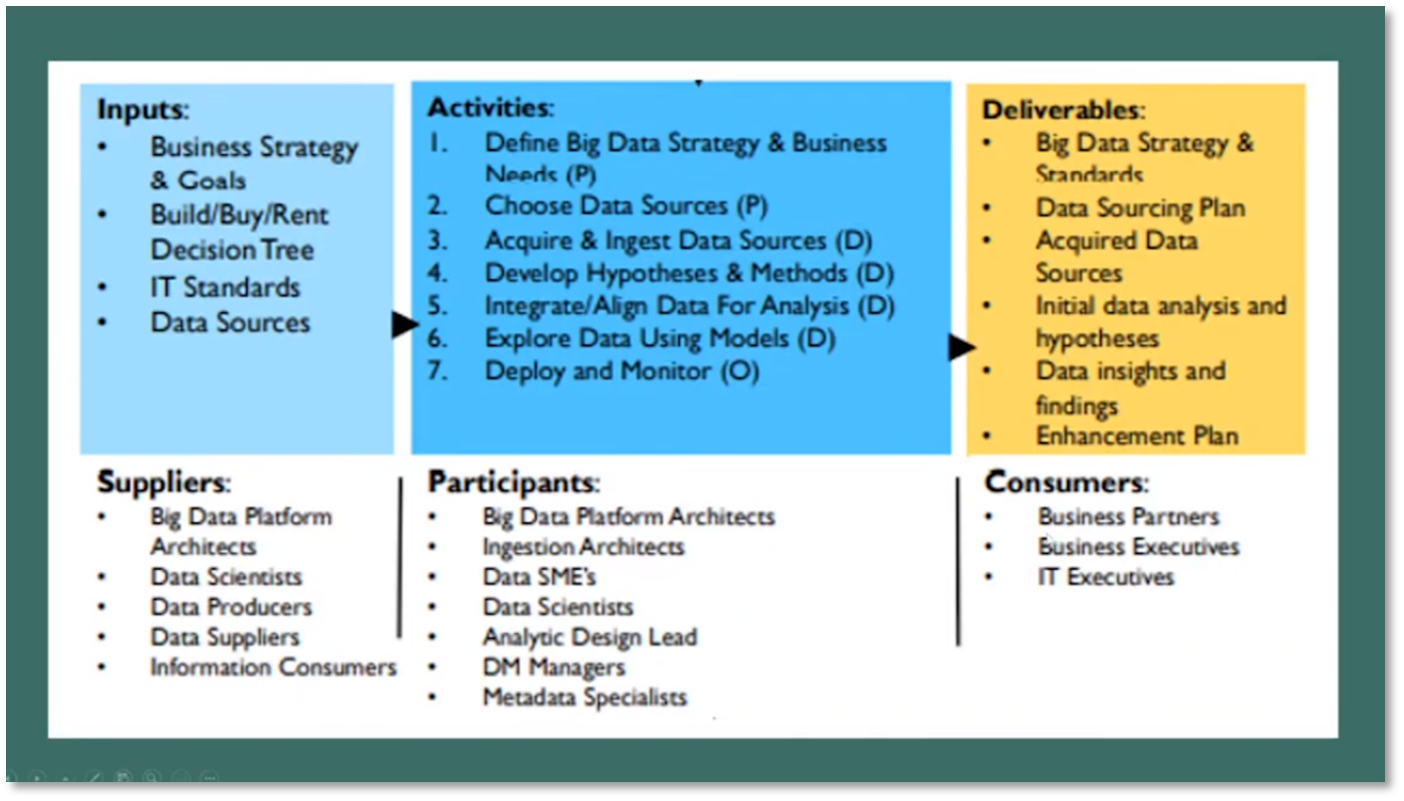
The balanced scorecard framework encompasses four critical areas: customer, financial, employee, and process. Employees are aligned with processes, which are aligned with customers, and eventually with financials based on the value proposition. The North Star metric should be aligned with the value proposition and customer, and OKRs should define the desired outcomes. Additionally, focusing on the jobs to be done by the customers and employees is crucial. It's important to bring in a psychologist to discuss motivating people to change, and culture measurement and change in the operating model should be prioritised. Different data types should be leveraged to find answers and insights for unknown questions. Understanding the relationship between metrics and known questions, data and its relationship to the business, and factors affecting the business are all essential goals for data analysis.
Figure 17 Inputs, Activities and Deliverable for Big Data and Data Science
Figure 18 Business Drivers: Answers & Insights
Figure 19 DIKW (Data, Information, Knowledge and Wisdom)
Big Data Context Diagram and Analytics
Big data and analytics are used to find answers and insights for questions that are not known at the start of the analysis. Its result is to enable business executives and management partners to measure and analyse performance. This process involves understanding why events occurred, forecasting future effects, operational optimisation, and identifying unknown factors. The sophistication and maturity of data play a crucial role in answering questions and managing risks associated with big data.
Figure 20 Degree of Separation determines the risk of Big Data
Figure 21 OMTM Questions & Decisions: Knowledge
Alignment of Business Strategy and Data Metrics
To achieve business goals, aligning decision-making with data metrics is important. However, if the data is not up-to-date, it can lead to a separation between what the business wants to achieve and what the data can answer. To avoid this, businesses must educate themselves about how data can provide and connect top-level metrics and strategy to the department or project level. Finding the right metrics is key to driving change and supporting decision-making, and opening discussions with business architects to address any misalignment is crucial for progress.
Aligning Data with Business Metrics
Businesses need to actively engage with data and insights to achieve alignment with their metrics and targets. However, many companies find that the produced information does not lead to any changes, indicating a need for communication, education, and change management. Executives also require defined metrics and an understanding of critical data elements to comprehend the direction of the business. Aligning data with business metrics can be done effectively by demonstrating how data analysis can add value to the organisation, especially by relating it to spending.
Importance of Metrics and Financial Value in Data Management
The importance of producing valuable insights and assessing whether the insights produced are worth the investment is emphasised. Howard notes that business decisions are often influenced by metrics and financial value, which can lead to potential budget cuts for IT departments. To achieve alignment between departments, demonstrate data management programs' financial impact and value by linking financial spending to achieving tangible value. Howard highlights the significance of measuring customer satisfaction and connecting data to customer churn rates and the overall customer lifecycle. To ensure data management programs' success, formalise the metrics definition and align data with business expectations. Howard stresses connecting data with answering metrics and driving the desired outcomes, highlighting the significance of aligning decisions with the defined metrics.
Aligning Metrics and Value Propositions in Business Strategy
Alignment of data is crucial to drive a specific metric, be it financial, sales, or customer churn. While money is a necessary indicator for alignment and progress, it should not be the sole north star but rather an indicator to begin aligning efforts. Spending large amounts on infrastructure without bringing value to the company may be counterproductive. Therefore, ensuring alignment in spending can lead to cost savings and better products for customers. To achieve this, the North Star should align with the value proposition, which ultimately drives the end result of money.
Importance of Value Proposition and Correct Metrics in Business
The key to increasing revenue is to deliver a value proposition by choosing the right metrics and aligning them to the North Star. However, regulators focus on risk and other factors like reputational issues instead of direct revenue. It is important to look at all aspects of justifying them to ensure that infrastructure costs bring in more revenue and increase the value proposition. Besides, data management programs must align with business value and be properly measured for necessary improvement. Communication and collaboration among data professionals and other departments are crucial for progress. Howard highlights the need for better communication and cooperation between data professionals and other business departments, emphasising the importance of teamwork and collaboration.
The Uncertainty Framework and Team Structure
The uncertainty framework is a tool to measure levels of uncertainty in cause-and-effect relationships. Different quadrants of the framework require different team structures. In a well-defined cause-and-effect scenario, the team structure is hierarchical with machine-based decision-making. In a complicated environment, expert advice is needed, requiring a smaller expert team. A team of people who can probe with hypothesis testing is needed in a complex scenario. Organisational culture, leadership, and people's appetite for risk also influence team structure in different uncertainty quadrants. Traditional data analysis does not yield answers in the chaos area, requiring leadership to navigate the situation.
Building Team Culture and Decision-Making in Business
Building a successful team culture in different business areas requires decision-making and using data to understand consequences. Howard notes that it is crucial to tailor the team and culture development approach to each area's specific needs and develop the work and leadership method that aligns with each business area's unique characteristics. Big data plays a vital role in decision-making as different technologies are needed for different cause-and-effect scenarios. However, it is important to understand that not every situation can be approached with the same analytics and methods. To develop a successful team culture in a business, it is crucial to understand the relationship between cause and effect and avoid the mindset of "we've always done it this way."
If you would like to join the discussion, please visit our community platform, the Data Professional Expedition.
Additionally, if you would like to be a guest speaker on a future webinar, kindly contact Debbie (social@modelwaresystems.com)
Don’t forget to join our exciting LinkedIn and Meetup data communities not to miss out!